Understanding the Decoy Effect in Consumer Choice
The decoy effect is a fascinating phenomenon in consumer psychology where adding a third option can significantly influence a customer’s choice between two initial options. Let’s explore how this cognitive bias works through the lens of mobile phone plans.
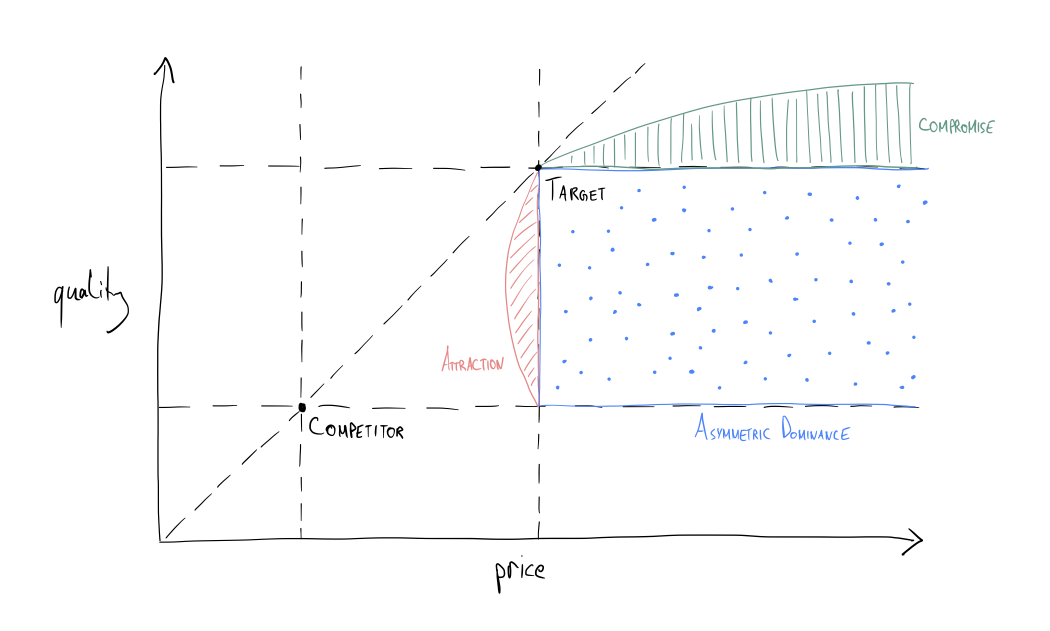
The diagram above illustrates the three different decoy effects on a quality-price grid. The competitor and target products are fixed points, with three distinct regions where placing a decoy product can influence consumer choice
The Basic Setup: Target vs Competitor
| Target | Competitor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | 30€ | 20€ | |
| # GB | 10 | 6 |
Asymmetric dominance
This occurs when we introduce a decoy that’s clearly inferior to our target product:
| Target | Competitor | Decoy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | 30€ | 20€ | 35€ |
| # GB | 10 | 6 | 9 |
Here, the decoy is both more expensive and offers less data than our target, making the target appear as a more rational choice.
Attraction effect
This subtle approach positions the decoy slightly below the target in both price and quality:
| Target | Competitor | Decoy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | 30€ | 20€ | 28€ |
| # GB | 10 | 6 | 7 |
The decoy’s presence makes the target’s premium features more attractive, despite its higher price point.
Compromise effect
This strategy positions the target as the “middle ground” option:
| Target | Competitor | Decoy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | 30€ | 20€ | 50€ |
| # GB | 10 | 6 | 12 |
By introducing a high-priced option, the target appears as a reasonable compromise between price and features.
Acknowledgement: Based on lecture notes from the winter term 2017/18 lecture Digital Communities at TU Berlin.